Products
INTERCEPT™ Blood System for Platelets
The INTERCEPT™ Blood System for Platelets is used by blood centres globally to help protect patients, improve availability, safeguard clinical outcomes and provide operational benefits
Protects Patients
Robust, Broad-Spectrum Pathogen Inactivation*
The INTERCEPT™ Blood System for Platelets is used to inactivate a broad spectrum of viruses, bacteria, and parasites, as well as contaminating donor leucocytes in platelet components; reducing the risk of transfusion transmitted infections (TTIs), including sepsis, and transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GVHD).1


- Acinetobacter baumannii†
- Anaplasma phagocytophilum (HGE agent)‡
- Enterobacter cloacae†‡
- Escherichia coli†‡
- Klebsiella pneumoniae†‡
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa†‡
- Salmonella choleraesuis†‡
- Serratia marcescens†‡
- Serratia li quefaciens†‡
- Yersinia enterocolitica†‡
- Bacillus cereus (vegetative)†‡
- Bifidobacterium adolescentis†
- Clostridium perfringens (vegetative form)†‡
- Corynebacterium minutissimum†‡
- Cutibacterium acnes†‡
- Lactobacillus species‡
- Listeria monocytogenes†‡
- Staphylococcus aureus†‡
- Staphylococcus aureus MRSA‡
- Staphylococcus aureus MSSA‡
- Staphylococcus epidermis†‡
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Streptococcus mitis†‡
- Streptococcus pneumoniae†‡
- Streptococcus pyogenes†‡
- Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease)†‡
- Treponema pallidum (syphilis)†‡
†Platelets in plasma/additive solution.
‡Platelets in 100% plasma.
Gram-negative, Gram-positive, spirochaetes
- HIV-1 IIIB, cell-associated†‡
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV)†‡
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV)†‡
- Duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV, model virus for HBV)†‡
- Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV, model virus for HCV)†‡
- Human T-cell lymphotropic virus (HTLV-I and HTLV-II)†‡
- West Nile virus (WNV)†‡
- Chikunguyna virus (CHIKV)†‡
- Dengue virus (DENV)†‡
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)†
- Pseudorabies virus (model for CMV)‡
- Avian influenza virus A (FLUAV)†‡
- SARS-CoV-2†‡
- Yellow fever virus (YFV)†‡
- Zika virus (ZIKV)†‡
- Bluetongue virus (model for non-enveloped virus)†‡
- Human adenovirus 5 (Ad5)†‡
- Feline calicivirus (FCV)†‡
- Parvovirus B19‡
†Platelets in plasma/additive solution.
‡Platelets in 100% plasma.
- Babesia microti (babesiosis)†‡
- Leishmania major Jish (amastigote stage)†
- Leishmania mexicana (metacyclic promastigote stage)†
- Plasmodium falciparum (malaria)†‡
- Trypanosoma cruzi (Chagas’ disease)†‡
†Platelets in plasma/additive solution.
‡Platelets in 100% plasma.
- Human T-Cells†‡
†Platelets in plasma/additive solution.
‡Platelets in 100% plasma.
Learn more about pathogen inactivation efficacy
 Improve availability
Improve availability
A Proactive Approach to Pandemic Preparedness
The availability of safe blood products is critical to achieve optimal patient outcomes. However, blood is becoming an increasingly scarce resource and blood supplies continue to be threatened by a myriad of challenges. The INTERCEPT™ Blood System has demonstrated to help maintain continuity of patient care by helping to ensure platelet transfusions remain safe and accessible to patients during outbreaks or epidemics.2,3,4

 Safeguard Clinical Outcomes
Safeguard Clinical Outcomes
Proven in Routine Use
By reducing the risks of TTIs and certain undesirable adverse events, the INTERCEPT™ Blood System contributes to timely and safe blood transfusions while providing therapeutically effective products. INTERCEPT™ Platelets may be prescribed and transfused in accordance with standard transfusion methods.

 Provide Operational Benefits
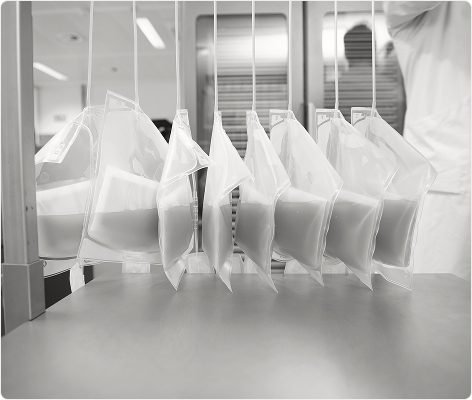
Provide Operational Benefits
Realise significant operational efficiencies at many steps of the transfusion chain
Though operational practices vary from centre to centre, the routine use of the INTERCEPT™ pathogen inactivation technology has demonstrated significant operational gains that translate to savings which offset partially or completely the investment cost. Historically, apheresis platelet concentrates were preferred over whole blood derived platelets to limit the donor exposure risk for patients, reducing the risk for transfusion-transmitted bacterial infections (TTBIs). As the INTERCEPT™ Blood System mitigates the TTBI risk associated with whole blood derived platelets, blood centres can shift their collection mix towards whole blood derived platelets which can be produced at a lower cost.

The INTERCEPT™ Blood System for Platelets
The INTERCEPT™ Blood System for Platelets consists of an INTERCEPT™ Processing Set for Platelets, which uses amotosalen (a photoactive compound), and the INTERCEPT™ Illuminator, a medical device providing an ultraviolet A (UVA) light source. Together they are used in the ex vivo preparation and storage of pathogen inactivated platelets intended for transfusion.
The INTERCEPT™ Blood System process is formed of 3 simple steps:
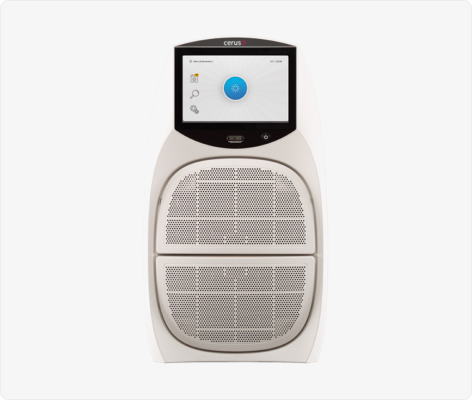

Introducing our next-generation LED-based illumination device
The INTERCEPT™ Blood System for Platelets now includes the new INTERCEPT™ Illuminator INT200. Designed to simplify operations, from start to finish, of the pathogen inactivation process.5
The current INTERCEPT™ Illuminator (INT100) was designed to deliver a controlled amount of ultraviolet A (UVA) light emitted by fluorescent bulbs. In recent years, the global lighting industry has experienced a shift from fluorescent bulbs to LED technologies. LED-based technology is utilised in the new replacement for the INT100, known as the INT200 illuminator.
A range of INTERCEPT™ Processing Sets are available to meet your platelet production needs
Platelets Small Volume (SV):
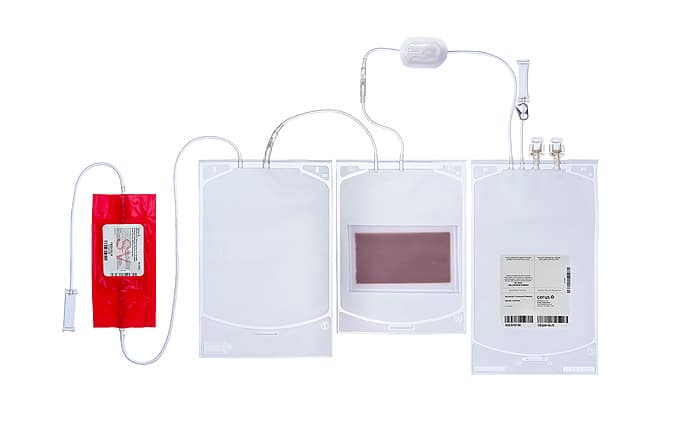

Platelets Large Volume (LV):
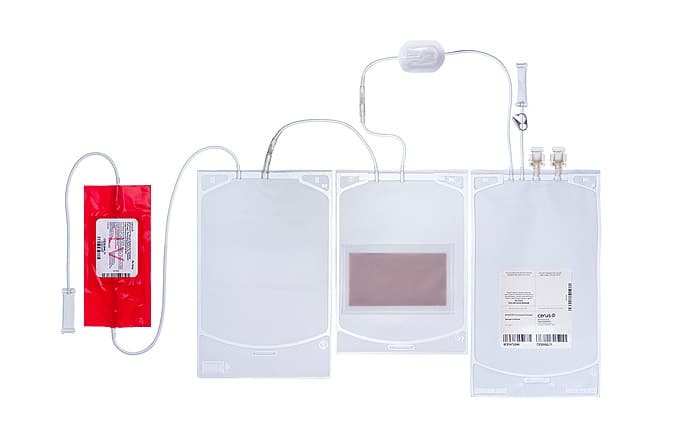

Platelets with Dual Storage (DS):
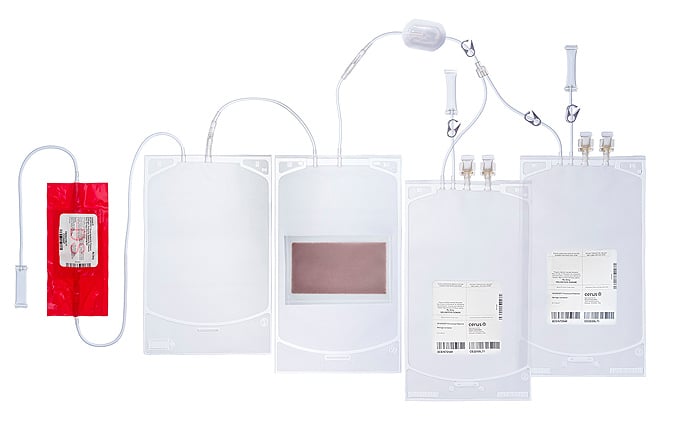

Implementing INTERCEPT
Our experienced deployment team is here to support in every step
The Cerus Deployment Team has been helping blood centres to successfully implement pathogen inactivation for over 10 years. The team is experienced in single centre, multicentre regional and country-wide implementations, and understands how to integrate the INTERCEPT™ Blood System into existing blood banking processes, managing implementation strategies which vary widely in complexity.

References:
- The INTERCEPT Blood System for Platelets Technical Data Sheet, Cerus Corporation.
- Rasongles P et al., 2009. Transfusion of platelet components prepared with photochemical pathogen inactivation treatment during a Chikungunya virus epidemic in Ile de La Réunion. Transfusion 49: 1083-1091
- Marano G et al., 2017. Ten years since the last Chikungunya virus outbreak in Italy: history repeats itself. Blood Transfus 15: 489-590
- Domanovic D et al., 2019. Pathogen reduction of blood components during outbreaks of infectious diseases in the European Union: an expert opinion from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control consultation meeting. Blood Transfus 17: 433-448
- Cerus data on-file: INTERCEPT LED Illuminator Summative Human Factors Validation Study Report (DES-HF 00557-02); INTERCEPT LED Illuminator Late Formative Study Report (DES-HF 00643-02)
There is no pathogen inactivation process that has been shown to eliminate all pathogens. Certain non-enveloped viruses (e.g., HAV, HEV, B19, and poliovirus) and Bacillus cereus spores have demonstrated resistance to the INTERCEPT™ process. For a full list of warnings, precautions for use and pathogens inactivated, please refer to the Technical Data Sheet and Instructions for Use found in the resource section of this website.